Exploring the Artificial Meat Market: A Comprehensive Introduction (Part I)
One of the biggest biotech trend !
Dear Readers,
Welcome to the SciX Newsletter! If you're just discovering SciX and curious about the types of articles we offer, please click here for a glimpse of what to expect.
In prior articles, SciX examined the science, key assets, clinical trials, technological challenges, and market viability of multiple companies developing engineered personalised therapies (CAR-T, CAR-NK, CAR-MAC, and CAR-Treg) for haematological and a variety of solid cancers. These articles are available for subscribers and can be found under archived articles.
If you haven't yet subscribed to the SciX newsletter, we invite you to do so now. Just enter your email address below, and you'll be among the first to know when we publish new content.
Moving forward, we are shifting or focus to the Artificial-Meat Market, recognised as one of the top five biotech trends of 2022 by Forbes. Artificial-Meat production has emerged as a groundbreaking technology in the global food industry. We will examine this sector through the lens of science, helping investors understand the scientific foundations, any potential technological drawbacks, future prospects, and the overall financial viability of key players in this burgeoning industry.
1. The Rise of Artificial Meat Industry: An Overview
1.1 What is Artificial Meat ?
Artificial-Meat, also referred as Cultured Meat or Lab-Grown Meat and sometimes as Clean Meat as well as slaughter-free meat and ethically grown meat, is a revolutionary advancement of Cellular Agriculture (Cell Ag). Cell Ag is the production of animal-sourced foods, either acellular and cellular products from cell culture.
Acellular products like casein, rennet, vanillin, ovalbumin are made of organic molecules like proteins and fats and contain no cellular or living material in the final product.
Cellular products, on the other hand, like meat, leather, fur, wood are made of living or once-living cells.
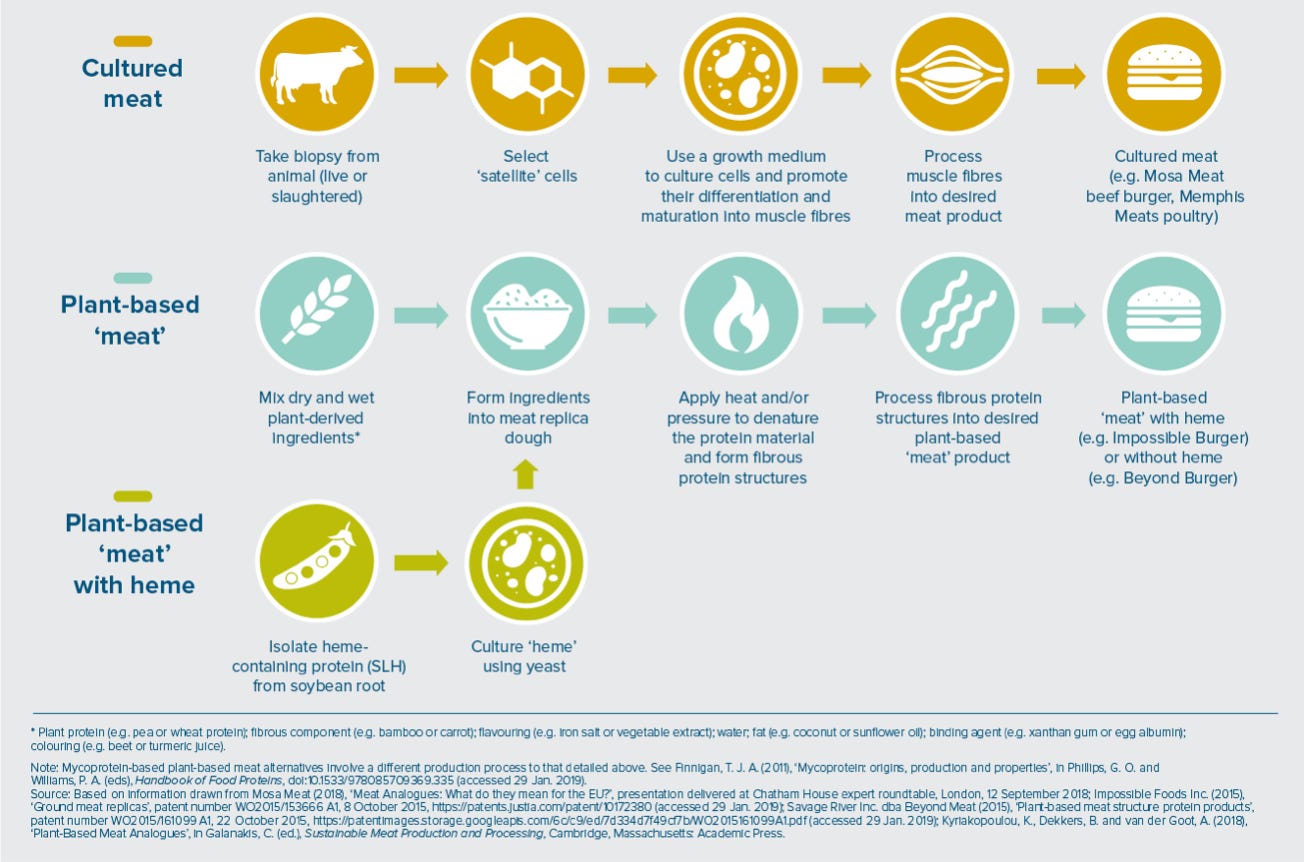
Artificial-Meat is not plant-based (though there are many hybrid products). It is not some kind of meat replacement like Beyond Meat or Impossible products (a fully engineered vegan alternative). Cell Cultured meat is meat, it is an animal-free, lab-grown product derived from animal cells. It is real animal tissue grown outside the animal itself. Different companies specializing in tissue engineering have produced beef, chicken, fish, and the much coveted bacon, among other products.
1.2 Brief History of Lab-Grown Meat
The idea of Lab-Grown Meat for human consumption was recorded in Winston Churchill’s essay “Fifty Years Hence” which was later published in the book “Thought and Adventure” in 1932.
In 2012, scientist at Maastricht University, Netherlands Mark Post (co-founder and CSO of Mosa Meat) launched the world’s first artificially cultured meat after 6 years of research. He produced the first cow-less burger, which was tasted live in London back in 2013. That first burger cost a massive €250,000 to grow, which was financed by Sergey Brin, co-founder of Google. In two years, the cost of a single, lab-grown beef patty dropped to around €10. During this 2 year period, four new cultivated meat companies were founded, which helped to bring the price of lab-grown meat down. The few early investors of Artificial-Meat industry were Bill Gates, Biz Stone and Richard Branson.
Regionally, North America is projected to dominate the cultured meat market in 2021. The market is also expanding into Asia, since China’s signature in 2017 of a US $300M agreement to import cultured meat technologies from Israel. Additionally, in Nov 2019, scientist Guanghong Zhou obtained China’s first piece of cultured meat (5 g) by culturing porcine muscle stem cells. The Japanese government’s participation in May 2018 in a US $2.7M funding round for a new ‘clean meat’ start-up, Integriculture. Later, in March 2019, Nissin Foods, a famous Japanese food company, announced partnership with the University of Tokyo to produce cultured-meat.
It is estimated that the value of the global cultured meat market could reach US $20M by 2027.
1.3 What led to major price drop of lab-grown meat in just 2 years from its launch in 2013:
Technological advancements: As with many new technologies, the initial development of lab-grown meat was expensive and inefficient. Over time, researchers made significant progress in streamlining the production process and improving the technology, which led to cost reductions.
Economies of scale: In the initial stages, the production of lab-grown meat was on a very small scale, which typically results in higher costs. As the production process was refined and scaled up, the costs decreased due to the benefits of mass production.
Increased funding and investment: The interest in cultured meat grew as more people recognized its potential to address various issues, such as sustainability, animal welfare, and food security. This led to increased funding and investment in the field, enabling more research, development, and commercialization efforts, which helped drive down costs.
Improved cell culture media: One of the major costs in producing lab-grown meat is the cell culture media used to grow the cells. Over time, researchers developed more efficient and cost-effective culture media, which significantly reduced the overall cost of production.
Competition: The success of Post's initial lab-grown burger attracted other companies and researchers to the field, spurring competition and innovation, which further drove down costs.
2. Market Landscape and Key Players
Since the launch of Mosa Meat’s cultured beef patty in 2013, Artificial-Meat market has grown to more than 99 companies, each aiming to advance this industry. Additionally, nearly 40 life science firms have declared and formally launched products to supply market competitors with the essential inputs they need to support cultured meat and seafood production (Global Cultured Meat Market Analysis Report 2022).
Here are the names of Cultured-Meat Companies: 3D Bio-Tissues Ltd., Agulos Biotech LLC, Aleph Farms, Alife Foods, Ants Innovate, Artemys Foods, ArtMeat, Atomico, Avant Meats Company Limited, B.I.F.E. Laboratorios-Craveri, Back of the Yard Algae Sciences, Balletic Foods, Because Animals, Bene Meat Technologies AS, Biftek Inc., BioBQ, BioFood Systems, BioMilk, Ltd., BIOMILQ, BioTech Foods, Blue Ridge Bantam, BlueNalu Inc., Bluu Biosciences, Boston Meats Inc., Bruno Cell SRL, Cargill, Cass Materials Pty Ltd., CELL AG TECH, Cell Guidance Systems Ltd., CELLINK, Cellivate Technologies, CellMEAT, Celltainer Biotech BV, Cellular Agriculture Ltd., CellulaREvolution, CellX, Clear Meat Private Limited, Core Biogenesis, Cubiq Foods, Cultured Blood, Cultured Decadence, DaNAgreen Co. Ltd., Defined Bioscience Inc., DFJ, Dipole Materials, Diverse Farms, East Just Inc., Finless Foods Inc., Fork & Goode, Future Fields, Future Meat Technologies, Gelatex Technologies Ltd., HCS Pharma, Heuros, HigherSteaks, Hoxton Farms, Incuvers Innocent Meat, UG IntegriCulture Inc., Jellatech JOINN Biologics, KosmodeHealth Lab Farm Foods, Luyef Biotechnologies, Magic Valley, Pty, Ltd., MagicCavier, Matrix Meats, Meatable, Memphis Meats, Mirai Foods AG, Mogale Meat Co., Mosa Meat, Multus Media, MyoWorks, Pvt. Ltd., Mzansi Meat Co., New Age Meats, Novel Farms, Inc., NUProtein Co., Ltd., Orbillion Bio, ORF Genetics Ltd., Ospin Modular Bioprocessing, Peace of Meat, Perfect Day Foods, Roslin Technologies Ltd., Shiok Meats, SingCell Tx Pte. Ltd, SunP Biotech, SuperMeat, Tantti Laboratory, Inc., TeOra, Tiamat Sciences, TissueByNET Co. Ltd., TurtleTree Labs, Tyson Foods, Umami Meats, Unicorn Biotechnologies, Vivax Bio, Vow, White Board Foods, Wildtype.
Cultured meat market is a nascent industry, 2020 was a landmark year because a cultured chicken product developed by the company Eat Just made its debut on a restaurant menu in Singapore, after the country's food agency approved its sale to the public. The regulatory approval of this cellular food product within Singapore provides hope that other regulatory approvals could follow worldwide.
3. Benefits of Artificial-Meat Production ?
Lab-Grown Meat industry has potential to hugely reduce the amount of energy, land, and water utilized by the livestock industry. It is estimated that Cultured Meat can reduce land use by 99%, water use by 96%, and energy consumption by 45%.
Lab-Grown Meat has also been shown to reduce carbon footprint up to 92%, 52%, and 17%, air pollution up to 93%, 49%, and 29%, compared to conventional beef, pork, and chicken, respectively. As well as reduction in the methane emissions, which are recognized as a leading cause of climate change!
Lab-Grown Meat is safer, purer product, and a more consistent supply. This is because the product is being produced in safe, sterile, controlled conditions.
Another exciting aspect of Lab-Grown Meat is the ability to design and tune its constituents to make it healthier. For instance, you could make meat with fewer saturated fats and more unsaturated fats.
It is further surmised that the production of Lab-Grown Meat can solve the global hunger challenge. Livestock provides 25% of total protein in the diet, the world's population is expected to increase to 11.2 billion by the year 2100. Compounding this situation, the United Nations estimates that by 2050 there will be 2 billion hungry people in need of nutrition. Lab-Grown meat can be an environmental friendly and cost effective alternative way to produce protein dense food to feed a lot of people.
Finally, due to limited human–animal interaction the risk of zoonoses and other diseases will be decreased.

Fig. 5 Environmental Impact of Regular Meat vs Cultured Meat | Source: Article
4. How is Artificial Meat Produced ?
The process of making tissue outside the body is called Tissue Engineering. Theoretical foundation of Artificial Meat was laid with the discovery of Stem Cells.
Tissue Engineers grow the cells from a particular species on a scaffold (which helps to hold those cells in place), with serum (food for the cells to feed on while they grow) in an environment that promotes growth so that they can eventually grow into something that looks like a steak or a piece of chicken, for example.
The process of generation of Artificial Meat typically involves the following steps:
Cell selection: Muscle cells, such as satellite cells or stem cells, are isolated from a live animal through a small biopsy. These cells have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into muscle tissue.
Cell culture: The isolated cells are placed in a nutrient-rich cell culture media that provides the necessary conditions for cell growth and proliferation. The media usually contains essential nutrients, growth factors, vitamins, and minerals that mimic the environment inside an animal's body. The cells are then placed in a controlled environment, such as a bioreactor, where they can grow and multiply.
Differentiation and Maturation: As the cells multiply, they form muscle fibers or myotubes, which eventually develop into muscle tissue. This process is facilitated by providing the appropriate mechanical and biochemical cues. For example, researchers may use a scaffold or biodegradable structure to help the cells organize and form the desired tissue structure. In some cases, electrical stimulation or mechanical stretching is applied to promote the development of muscle tissue and improve its texture.
Harvesting: Once the cultured meat has reached the desired size and maturity, it is harvested, combined with other ingredients (such as fat cells, blood vessels, and connective tissue, which may also be cultured), and processed to create the final meat product. This product can then be cooked and consumed like conventional meat.
Scaling up: The process is optimized and scaled up to produce larger quantities of lab-grown meat at a commercially viable cost.

5. Challenges facing the Artificial Meat Industry
Production cost: The initial cost of producing cultured meat has been significantly higher than conventional meat production. Although the cost has decreased over time, it is still a challenge to make cultured meat financially competitive with traditionally sourced meat.
Scaling-up production: Scaling up the production process to meet global demand is a significant challenge. The industry needs to develop methods to produce larger quantities of cultured meat efficiently while maintaining quality and consistency.
Consumer acceptance: Public perception and acceptance of artificial meat is a critical factor in its success. Some consumers may be hesitant to consume cultured meat due to concerns about taste, texture, safety, or ethical considerations.
Regulatory approval: The artificial meat industry is subject to regulatory approval from agencies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The process of obtaining approval can be time-consuming and uncertain.
Technological challenges: The industry needs to overcome various technical challenges, including optimizing cell lines, developing suitable growth media, and refining bioreactor designs, to make cultured meat a viable option on a large scale.
Competition with plant-based alternatives: Cultured meat faces competition from plant-based meat alternatives, which have gained significant market share and consumer acceptance in recent years.
Intellectual property and patents: As with any emerging industry, the development of intellectual property and patents can be a challenge, as companies compete for market share and exclusive rights to new technologies.
Ethical concerns: While cultured meat is often considered more ethical than traditional meat production, some people still express concerns over the use of animal cells and the potential for animal suffering in the production process.
6. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on Artificial-Meat Market
The COVID-19 pandemic has had both positive and negative impacts on the Artificial-Meat industry.
6.1 Positive impacts:
Increased awareness: The pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of traditional meat supply chains and the potential risks associated with zoonotic diseases. This has increased public awareness and interest in alternative protein sources, including cultured meat.
Investment and funding: In response to the challenges faced by traditional meat supply chains during the pandemic, investors and governments have shown increased interest in supporting the development of alternative protein sources, leading to more funding for cultured meat startups.
Accelerated adoption: With the disruptions in meat supply chains and concerns over food safety, some consumers have become more open to trying alternative protein sources, potentially accelerating the adoption of cultured meat once it becomes available.
6.2 Negative impacts:
Disruptions in research and development: Like many industries, the cultured meat sector has faced disruptions due to lockdown measures, social distancing requirements, and other pandemic-related restrictions. This may have slowed down research and development progress in some cases.
Funding challenges: While the pandemic has led to increased interest in alternative protein sources, some investors may have become more risk-averse or diverted funds to address immediate pandemic-related concerns, which could have impacted funding for cultured meat startups.
7. Consumer Acceptance
Understanding consumer acceptance and the market potential of artificial meat is crucial for the success of this emerging industry. In this section, we will discuss the factors affecting consumer perception, the current state of market acceptance, and the strategies employed to increase adoption.
7.1 Public Perception of Lab-Grown Meat
Taste, texture, and appearance: Ensuring that the sensory attributes of artificial meat closely resemble traditional meat is important for consumer acceptance. Companies invest significant resources in research and development to perfect the taste, texture, and appearance of their products.
Health and safety concerns: Some consumers may have concerns about the health and safety aspects of lab-grown meat. Addressing these concerns through transparent communication and rigorous safety testing can help build consumer trust.
Ethical considerations: Artificial meat may appeal to consumers who are concerned about animal welfare, environmental sustainability, or the ethics of traditional meat production. However, some people may still have reservations due to religious or cultural reasons.
7.2 Barriers to Adoption
Price: The current cost of lab-grown meat compared to conventional meat and the potential for cost reduction as the industry scales up.
Cultural and traditional factors: Resistance to change and the role of cultural norms and food traditions in consumer preferences.
Health and safety concerns: Perceptions about the nutritional value and safety of artificial meat compared to conventional meat products.
Labeling and marketing regulations: The impact of how lab-grown meat is labeled and marketed on consumer acceptance.
7.3 Strategies for Increasing Consumer Adoption
Education and awareness: Increasing consumer awareness about the benefits of artificial meat, such as its lower environmental impact and potential for improved animal welfare, can help drive acceptance.
Marketing and branding: Effective marketing and branding strategies can play a significant role in influencing consumer perception and adoption. Companies can use targeted messaging to appeal to different consumer segments based on their values and preferences.
Price competitiveness: Reducing the cost of lab-grown meat production to achieve price parity with traditional meat can help make artificial meat a more attractive option for a broader range of consumers.
Taste tests and product sampling: Offering taste tests and product sampling can help break down barriers and encourage consumers to try lab-grown meat, increasing the likelihood of adoption.
8. Future Outlook
Despite the challenges, the future for the cultured meat industry remains promising. As the world continues to face issues like climate change, food security, and ethical concerns related to animal agriculture, the demand for sustainable and efficient protein sources will continue to grow.
The cultured meat industry is expected to benefit from ongoing advancements in biotechnology, tissue engineering, and scale-up technologies. This will help in reducing production costs, improving product quality, and meeting regulatory requirements. As a result, cultured meat products are likely to become more widely available and affordable, leading to increased adoption by consumers.
Additionally, collaborations between cultured meat companies, investors, governments, and other stakeholders are expected to grow, further supporting the development and commercialization of cultured meat products in the coming years.
In the follow-up articles of this Artificial-Meat Market series, I will be profiling some of the promising companies… Stay-tuned!
I hope you've been enjoying SciX content and finding it informative and engaging. If you'd like to receive regular updates and never miss out on our latest articles, we encourage you to sign up for our newsletter.
Just enter your email address below, and you'll be among the first to know when we publish new content.






